OXYGEN INHALATION THERAPY

Oxygen inhalation therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is a medical treatment that provides extra oxygen to individuals who have difficulty breathing or have low blood oxygen levels, often due to lung diseases or other conditions.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
What it is:
- Oxygen therapy provides additional oxygen beyond what's normally inhaled from the air.
- It's a prescribed treatment, not a freely available option, and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
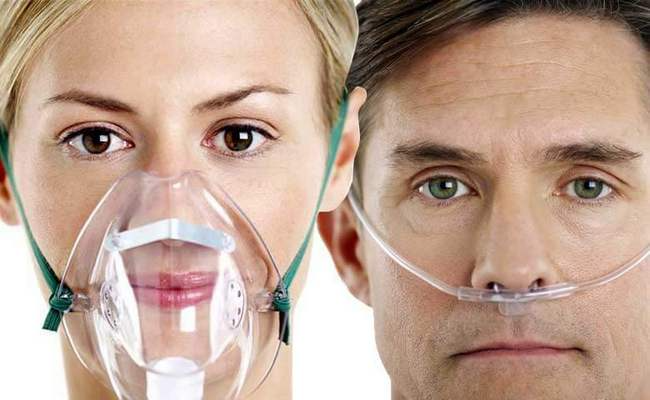
- Oxygen can be delivered through various devices, including:
- Nasal Cannula: Tubes that fit into the nostrils.
- Face Masks: Masks that cover the nose and mouth.
- Tents: Enclosures that cover the head and shoulders.
- Oxygen Concentrators: Devices that extract oxygen from the air.
- Tanks: Containing liquid or gas oxygen.
- Nasal Cannula: Tubes that fit into the nostrils.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Pulmonary fibrosis.
- Pneumonia.
- Heart failure.
- Severe long-term asthma.
- Pulmonary hypertension.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Breathing problems caused by obesity and underlying conditions.
- Hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels).
- Carbon monoxide toxicity.
- Cluster headache.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Improved oxygen levels in the blood.
- Reduced shortness of breath.
- Increased energy levels.
- Better sleep.
- Improved quality of life.
- Improved oxygen levels in the blood.
Important Considerations:
- Oxygen therapy should only be used with a prescription from a healthcare provider.
- Some individuals may require long-term oxygen therapy at home.
- It's crucial to follow your doctor's instructions on how to use oxygen therapy and to monitor your oxygen levels and overall health.
- While generally safe, oxygen therapy can cause side effects, such as nosebleeds and headaches.
- In some cases, oxygen therapy is administered in a hyperbaric chamber, which increases the pressure of oxygen delivered to the body.